
See Who is Logging in on Shared Windows Accounts
Need to accurately audit access logs across the network due to a shared computer? Not easy to track who is logging in when to which computer? Usually, admins can go to Event Viewer, Windows Logs > Security, then click on the event and you can see the username of the person that logged in for that event ID – very tedious to do. But, also, what if users logging in using shared Windows accounts? Then even thought you can see the username, you have no idea which person actually logged in. This does not meet regulatory compliance requirements regarding proper auditing.
Why do people still use shared accounts?
Users are sharing passwords for a variety of reasons:
- Save money on licensing. Some applications groups use a shared login to share a specific application that they all need access to. Instead of purchasing multiple licenses from the vendor, the group can save money by using a common login to share the resource between all the users that need access.
- Convenience over security. It’s easier to simply use an existing login than to go through the trouble of having to get your own access which may require the user to request permission by communication, wait, be asked ‘why’ and what not.
- Legacy reasons / old habits die hard. If a predecessor used many shared accounts, the next person may be tasked with unravelling the shared accounts still in use due to old habits.
Risks of shared computer and/or login accounts.
- Users need access to their desktop applications: having to memorize different kiosk computer login combinations, type, then do it again for the program is a huge waste of time.
- Low level of accountability: Less accountability when using a shared computer, but even more so when using a shared login account. Accountability is unacceptably low for everyone.
- Inaccurate computer log auditing: Clean audits are impossible since everyone logging in is using the same login. When a data breach incident occurred, who logged in suspiciously? The username might simply be “PC2” and password “123password”.
- Compliance: Violation of compliance regulations and organization’s policies. Users must login with their own accounts, even on shared computers.
- Cost in time: Even on shared accounts, users may need to switch accounts for a particular application. The organization loses valuable time if each login process takes too much time and typing.
See who is logging in on shared Windows accounts.
Legacy shared Windows accounts on workstations continue to plague IT teams. The task required to completely transition all shared accounts over to individual may not be so simple in most cases. See how one clinic keeps clean audit trails on shared accounts using GateKeeper in this healthcare IT case study. IT admins can run reports to show all login events by computer, by user, and more.
See active sessions in real-time by username on any shared computer.
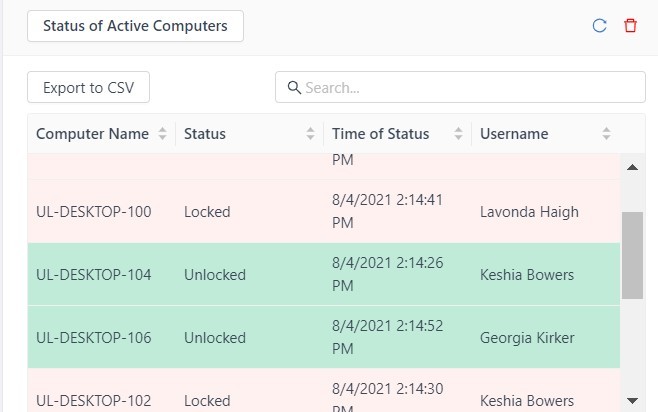
GateKeeper’s identity access management auditing accurately audits access logs. IT admins can also see a real-time list of active user sessions. Below is a screenshot from the GateKeeper admin console that shows Lavonda’s computer is currently locked while Keshia and Georgia are currently logged in and active. Keshia is currently working on computer UL-DESKTOP-104. Don’t let a shared computer ruin the auditing. Read other GateKeeper reviews from happy clients that can accurately see computer logs for access control and security.
Finally, see GateKeeper Enterprise advanced MFA in action.
Take a self-guided tour of how you can evolve from passwords. Then you're really saving time with automation.




