
What is an Advanced Persistent Threat?
Advanced Persistent Threats explained.
Advanced Persistent Threats (or “APTs”) are a dangerous form of cyber attack where a team of intruders use sophisticated hacking techniques to establish a long-term presence on a network. Their intention is usually to breach highly sensitive data and their methods are always evolving. These APT attacks usually come from very powerful cyber gangs, nations, or expert cyber criminals.
As the name indicates, this type of cyber attack employs an advanced, clandestine campaign against carefully chosen targets, mostly government networks and large corporations to cause destructive consequences. Therefore, IT admins need to defend their networks proportionately.
Advanced Persistent Threat Targets
Professional cyber criminals, likely backed by government agencies, choose high-level targets for espionage attacks. The attack is supported with extensive research and resources. The ultimate goal of getting access and then stealing confidential information over the long term instead of a quick ransomware.
Statistics show that APT attackers start use smaller companies to gain access to and launch an attack on larger firms. Often, these companies have less sophisticated and weak defenses against cyber attacks. Cyber criminals will use these weak defenses as stepping stones for bigger targets. Attack methods of these cyber criminals vary and can include social engineering, bots, malware attacks, physical theft, and more.
Although corporations and national-level organizations are the primary targets of APT assaults, many small- and medium-sized businesses are also vulnerable. Every business should always be ready to ward off ATP attacks by sophisticated cyber criminals.
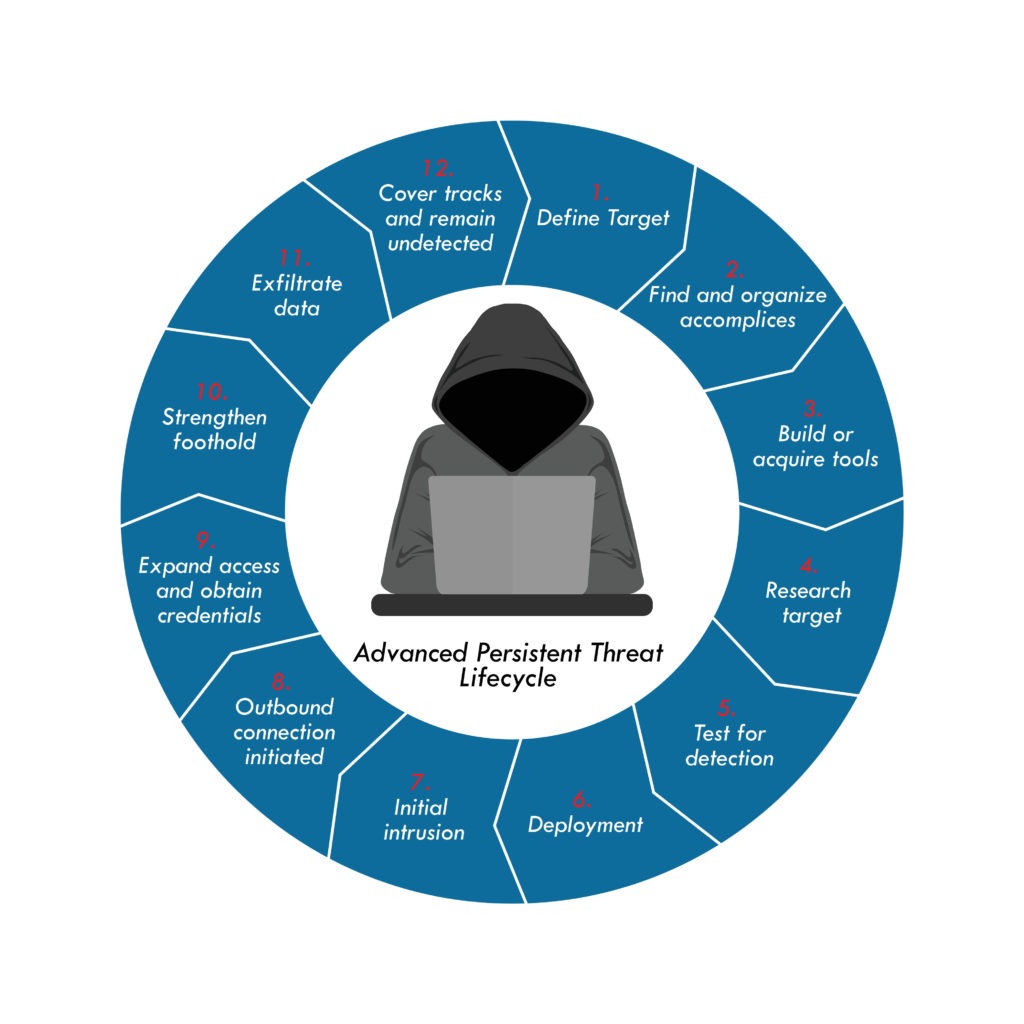
Stages of A Successful Advanced Persistent Attack
The cyber criminals execute successful APT attacks in five stages:
- Infiltration
- Strengthening Foothold
- Expand Access
- Move Laterally
- Extraction
Network Infiltration
Firstly, cyber criminals can infiltrate via common cyber activities like using infected files, junk email, vulnerable, apps, human resources, malicious uploading, social engineering, or phishing attacks. There are endless ways to infiltrate: people, computers, websites, compromised software, compromised extensions, and more. Therefore, the attack vectors are numerous and the window is wide.
Strengthening Foothold
Secondly, once the attackers successfully breach a network, they move quickly to create a backdoor shell or malware that gives them backdoor access for operations. The goal of an APT attacks is to stay inside the network undetected as long as possible to maximize their theft/damage.
Expand Access
The next step is to broaden the access within the system. Often, this is done by using password-cracking mechanisms to gain administrative privileges and rights. This compromises employees access to sensitive data, then moves up the firm’s hierarchy.
Move Laterally
After securing the network, the cyber attackers can now move around at will and try to gather the confidential data they need. They can also expand the cyber attack on other secure parts of the network. They can also attack servers connected with the infected server they have already compromised. Afterwards, there comes the final phase of the APT attack: extraction.
Extraction
The APT attackers can now try to understand and exploit the vulnerabilities of the network and steal the information. Depending on their goals, the cyber attacker can choose whether to stay in the system until exposed or leave once the objective is accomplished. However, they can still leave malware as a backdoor channel for future entrance (as they often do).
See GateKeeper Enterprise advanced MFA in action.
Take a self-guided tour of how you can evolve from passwords. Then you're really saving time with automation.




