
What is NFC technology?
Purpose and Function
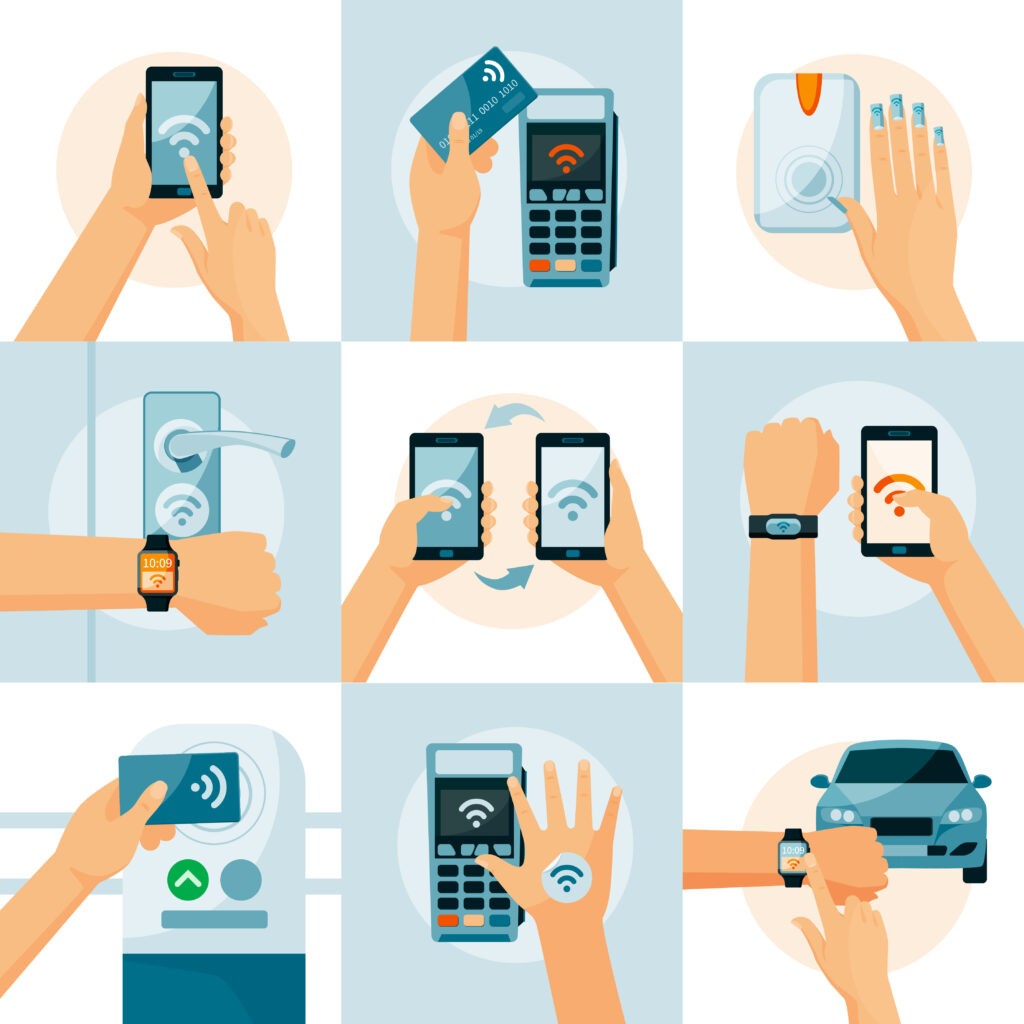
NFC, or "Near Field Communication" technology is a form of wireless communication that allows devices to exchange data. Though unlike Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, NFC compatible devices must be in very close proximity to each other to interact. Because of its versatility, it has been implemented into a wide range of devices, including smartphones, collectibles, gaming systems, and access control solutions.
Approved as an ISO/IEC standard in 2003, NFC is based on RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification), but has an even shorter transmission range. They both rely on the principle of inductive coupling, where devices use a coil to induce an electric current with a magnetic field emitted by a reader. This allows for the wireless transmission.
Application
NFC technology has seen three mainstream modern applications:
- Data Transfer - There are three main supported modes of data transfer.
- Read/Write - Allows users to read from and write to NFC chips to store information.
- Card Emulation - Allows an enabled device to become a proxy for more traditional contactless cards.
- Peer-to-Peer - Allowing two enabled devices to exchange data with one another.
- Access Management - Used to enforce access credentials at worksite or work system entry points via user-held tags.
- Contactless Payment - Used commonly in smartphones, smartwatches, and contactless payment cards via NFC-enabled payment terminals.
Enterprise 2FA and password manager. One key for all your passwords. Experience fully automated login and security. For example, faster MFA, auto-OTP, password manager, and worry-free workflow with proximity-based privileged access management for Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, VPNs, websites, and desktop applications including MES, EHR, CAD, and more. Overall, a massive upgrade to security and efficiency.
or call 240-547-5446

